MATTER AND ENERGY
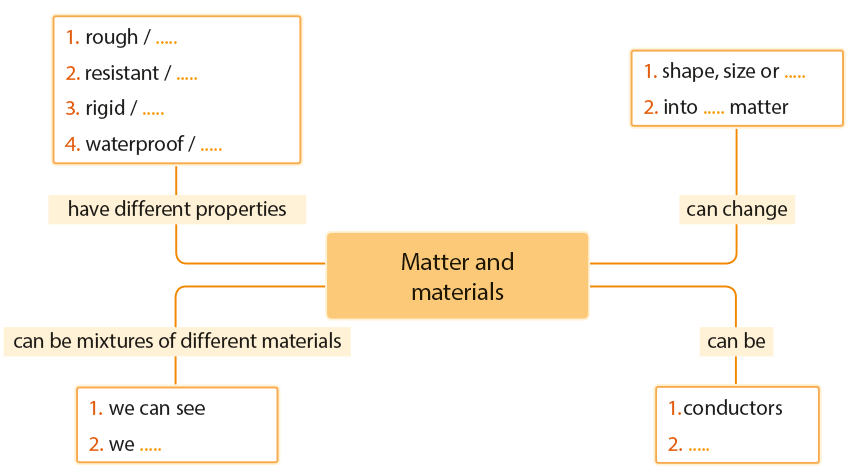
What is matter? Anything we can see, touch, taste or smell is matter. In other words, everything on our planet and in the Universe is made up of matter. Even you are made up of matter!
The words matter and material can be confusing. Materials are made up of matter, and we use materials to make things.
The words matter and material can be confusing. Materials are made up of matter, and we use materials to make things.
- Copy and complete the project in your notebook. Add two more objects and the words to describe them.
- Carla wants to add the word resistant to some of the objects. Which objects?
- All of these objects are made up of different materials (metal, plastic, wood, etc.). Where do we get them from?
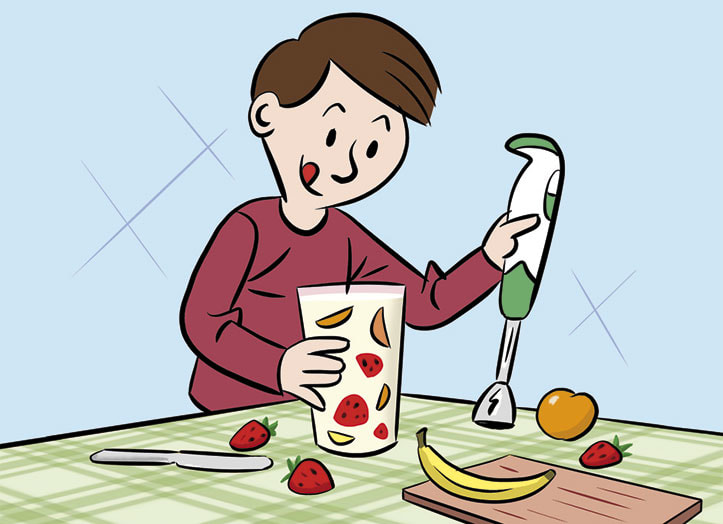
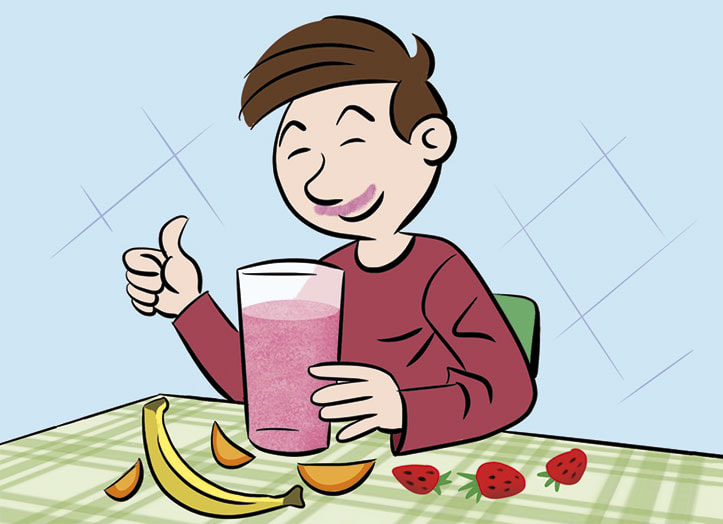
A mixture is something that contains two or more different materials. Almost everything around us is a mixture, including the air we breathe. In some mixtures we can see the different materials; in others it is impossible to see the different materials. Try making the mixtures below – some of them are delicious,
Do you think it is possible to separate the different materials in a mixture? We can separate some materials in a mixture by sieving, filtering or evaporating. Follow the steps below and learn about these three methods.
- Describe the two types of mixtures in your own words.
- Put the following mixtures into two groups: sea water, muesli, milkshake, paint, fruit cake.
- Which separation method do you think is best for separating sand and water? What about sand and pebbles?
- Use drawings to explain the difference between filtering and sieving.
Energy is important for everything we do. But did you know that energy has different forms? Look at the picture and read about the different types of energy that we find all around us.
When we heat a material, we are adding thermal energy to it. Thermal energy can make materials change state.
- If the thermal energy in a solid increases, it may become a liquid. This process is called melting.
- If the thermal energy in a liquid increases, it may become a gas. This process is called evaporation.
One of the properties of materials is the way they respond to electricity.
- Electricity can pass through some materials very easily. These materials are called electrical conductors. Metals and water are very good electrical conductors.
- Other materials don’t allow electricity to pass. These materials are called electrical insulators. Wood and plastic are good electrical insulators.
Why is it important to cover electrical cables in plastic?
Have you ever thought about why umbrellas, raincoats and rubber boots protect us from the rain?
We use different materials because of their properties. Look at the objects in the pictures. Think about what they are made of and why we use these materials. Use the words to help.
We use different materials because of their properties. Look at the objects in the pictures. Think about what they are made of and why we use these materials. Use the words to help.
What is matter?
Matter is everything around you. Atoms and compounds are all made of very small parts of matter. Those atoms go on to build the things you see and touch every day. Matter is defined as anything that has mass and takes up space (it has volume).
What is mass?
Mass is the amount of matter in an object. You might have a small object with a lot of mass such as a statue made of lead (Pb). You might have a large object with very little mass such as a balloon filled with helium (He). You should also know there is a difference between mass and weight. Mass is a measure of the matter in an object while weight is a measure of gravity’s pull on an object.
What is volume?
Volume is the amount of space something occupies. Words such as big, little, long, or short are used to describe volumes. A marble takes up a small volume while a star occupies a large volume. Different states of matter will fill volumes in different ways.
What makes a state of matter?
It's all about the physical state and energy in the atoms and molecules. Think about solids. Physical properties of a solid often include "hard" and "brittle." Liquids are fluidy, move around a little, and fill up containers. Gases are always around you, but the molecules of a gas are much farther apart than the molecules in a liquid. If a gas has an odor, you’ll often be able to smell it before you can see it.
THE PLANT KINGDOM
Plants are all around us. They can be different sizes, shapes and colours. They are living things that perform three life processes: nutrition, interaction and reproduction. Plants are very important. They give us food, medicine and clothes. They also give us the oxygen we need to live. Can you think of more things that plants give us?
Look at the story. Then read the descriptions below and identify if they describe deciduous, evergreen or both trees.
- They lose their leaves in autumn.
- They have leaves like needles.
- A cone protects the seeds.
- The seeds grow inside the fruit.
- They have branches, roots, a trunk, and leaves.
Copy the sentences in your notebook and complete them with the words Leaves, Stems and Roots.
Choose a plant and draw it in your notebook. Label the parts of the plant.
Alex wants to add the word cone to the chart. What should he write about it?
Investigate! Do all plants grow from seeds?
There are many different types of plants which we can classify in different ways.
- Grasses or herbaceous plants have a soft stem. They are thin and flexible and usually short.
- Bushes have a thick, hard stem with low branches.
- Trees have one thick, hard stem called a trunk. They are the tallest plants and have high branches. Trees can be deciduous or evergreen.

Photosynthesis
How plants make their own food
The food we eat comes from plants, but how do plants get their food? Plants make their own food. To do this they need water, minerals, light and energy from the Sun and carbon dioxide.
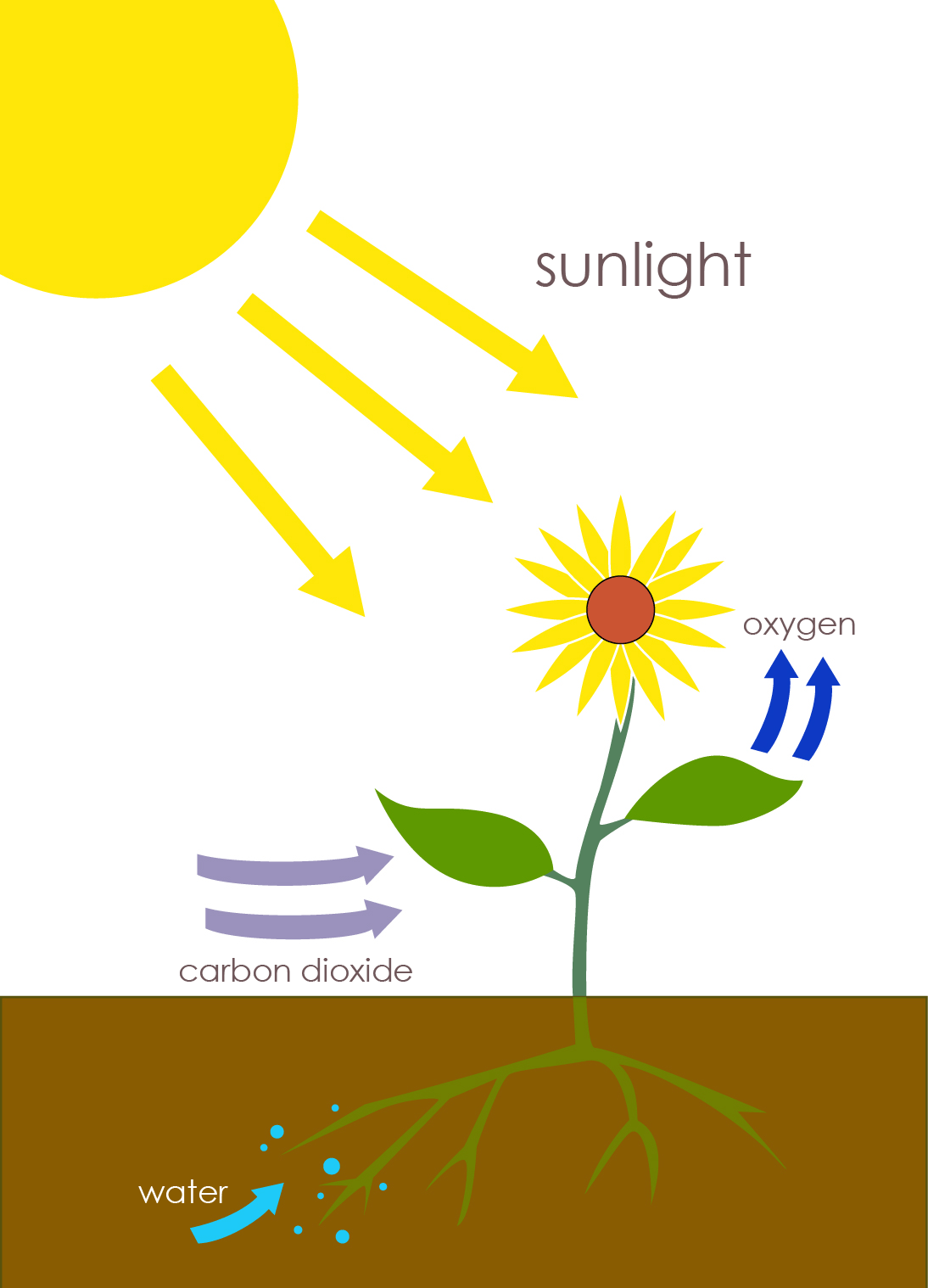
Respiration
Plants are living things and so they need to breathe, just like people and animals. During the day they can also use the oxygen they produce during the photosynthesis process. At night, however, they must take in oxygen from the air and release carbon dioxide.
How new plants grow
Plants can be classified as flowering or non-flowering plants. Let’s look at how flowering plants reproduce.


REPRODUCTION

- The first stage of reproduction in flowering plants is called ‘pollination‘.
- But what is pollination? This is when the pollen produced on the anther of a flower moves to the stigma.
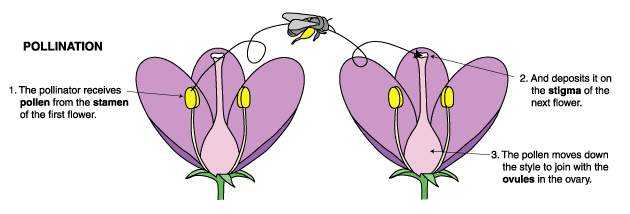
- If pollen moves from the anther to the stigma on the same flower (or a flower on the same plant), it is called ‘self-pollination’. If the pollen is transferred from the anther to the stigma on another plant, it’s called ‘cross-pollination’.
- There are two main ways that flowers are pollinated — by insects and by the wind. Insect pollinated flowers and wind pollinated flowers are adapted differently.
- Once the pollen grain lands on the stigma of the same species of plant a seed develops inside the ovary.
- Animal pollination is the transfer of pollen from the stamen to the stigma of another plant by an insect or bird.
- Wind pollination involves wind blowing the pollen from one plant to another.
- The first stage of reproduction in flowering plants is called ‘pollination‘.
- But what is pollination? This is when the pollen produced on the anther of a flower moves to the stigma.

- If pollen moves from the anther to the stigma on the same flower (or a flower on the same plant), it is called ‘self-pollination’. If the pollen is transferred from the anther to the stigma on another plant, it’s called ‘cross-pollination’.
- There are two main ways that flowers are pollinated — by insects and by the wind. Insect pollinated flowers and wind pollinated flowers are adapted differently.
- Once the pollen grain lands on the stigma of the same species of plant a seed develops inside the ovary.
- Animal pollination is the transfer of pollen from the stamen to the stigma of another plant by an insect or bird.
- Wind pollination involves wind blowing the pollen from one plant to another.
Copy and label the parts of a flower.
More than half our planet’s plant species live in rainforests.
Rainforests are also home to hundreds of species of animals.
They also clean the planet’s air. They take carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and release oxygen which we need for breathing.
Unfortunately rainforests are disappearing very
quickly. People cut down trees to make space for farming.
Today, many people, organisations and countries are trying to stop the destruction of the rainforests.
- Find out the names of the eight countries that the Amazon rainforest covers.
- Investigate the animals that are found in rainforests.
- Clavillia is a plant found in the rainforest. Research what this plant looks like and how people use it in medicine.
The Animal Kingdom is divided into two groups:
Invertebrates – All animals without back bones are called Invertebrates. Earthworms, starfishes, squids, snail fall in this category.
- Marine Invertebrates - There are a wide variety of interesting ocean animals that are invertebrates. These include sponges, corals, jellyfish, anemones, and starfish.
- Mollusks - Mollusks have a soft body that is covered by an outer layer called a mantle. Many mollusks live inside a shell, but not all of them. Some examples of mollusks include squid, snails, slugs, octopuses, and oysters.
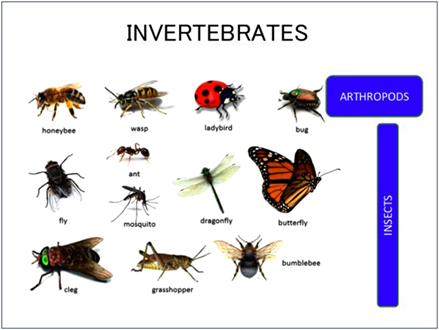
Vertebrates – All animals with back bones are called vertebrates (mammals, birds, fish, amphibians and reptiles).

Mammals are a particular class of animal.
What makes an animal a mammal are several things.
First, they must have glands that give milk. This is to feed their babies.
Second, they are warm-blooded.
Third, all mammals have fur or hair.
Humans are mammals and so are dogs, whales, elephants, and horses. Most mammals have teeth with the exception of the ant eater which doesn't have any teeth.
Where do they live?
Mammals live in all sorts of environments including the ocean, underground, and on land. Some mammals, bats for example, can even fly.
Other intelligent mammals include the dolphin, the elephant, the chimpanzee, and the pig. That's right, pigs are thought to be one of the smartest animals!
What is it that makes an animal a bird?
The main characteristic of a bird is feathers. No other animal has feathers. Other important features for birds are wings and hollow bones. Birds also lay eggs, like reptiles, however they are warm-blooded, like mammals.
Feathers are important to birds because they keep them warm, help them to fly, and provide camouflage.
There are all sizes of birds. Hummingbirds are some of the smallest birds, while ostriches are some of the biggest.
What makes a fish a fish?
All fish are cold-blooded animals that live in the water. They have backbones, fins, and scales.
All fish have gills that allow them to breathe water. Just like we use our lungs to exchange oxygen for carbon dioxide from the air, the gills of a fish perform a similar function from water. So fish still need oxygen to live, they just get it from the water instead of the air.
- The biggest, or heaviest, fish is the ocean sunfish which can weigh as much as 5,000 pounds.
- The longest fish is the whale shark which has been known to grow to over 40 feet long.
- The fastest fish is a sailfish which can swim as fast as 68 miles per hour.
- The smallest fish is the dwarf goby at only 9mm long.
A lot of people like to have fish as pets. There are special aquariums and food you can get to take care of your fish. They can be fun to have and also beautiful to look at. Although they are fairly easy to take care of as pets, you will need to do some work. You need to keep the
What is a reptile?
Reptiles are animals that are cold-blooded. Most reptiles lay eggs and their skin is covered with hard, dry scales.
What does cold-blooded mean?
Animals that are cold-blooded don't automatically maintain a constant body temperature. They have to lay out in the sun to keep their body heat up, like Jack and Barbossa!
There are many types of reptiles. The main categories are snakes, crocodiles and alligators, turtles, and lizards. Reptiles can be found on every continent except for Antarctica.
What's the difference between reptiles and amphibians? There are a few major differences that separate reptiles and amphibians. Amphibians go through a larval stage, like the tadpole which turns into a frog. Reptiles don't do this. Also, their skin is different where reptiles have scales for skin, but amphibians have moist, glandular skin.
What are amphibians?
Amphibians are a class of animals like reptiles, mammals, and birds. They live the first part of their lives in the water and the last part on the land. When they hatch from their eggs, amphibians have gills so they can breathe in the water.
They also have fins to help them swim, just like fish. Later, their bodies change, growing legs and lungs enabling them to live on the land.
Amphibians have adapted to live in a number of different habitats including streams, forests, meadows, bogs, swamps, ponds, rainforests, and lakes. Most of them like to live in or near water and in damp areas.
UNIT 2: LOOK AFTER YOURSELF

UNIT 1: INTERACTION
PARTS OF THE BODY

THE NERVOUS SYSTEM

A healthy diet is a balanced diet.
Fruit and vegetables are full of vitamins, minerals and fibre. Fruit has quite a lot of sugar ,so try to eat more vegetables than fruit. Some examples include: broccoli, onion, pepper, carrots, spinach, apples, bananas, cherries, oranges, and many more!


Dairy products are made from milk .They are rich in calcium, which keeps our bones and teeth healthy. Cheese, yoghurt, and milk are dairy products.


Proteins and Iron help us build muscle and make us strong. Meat, fish, beans and eggs contain proteins and iron.


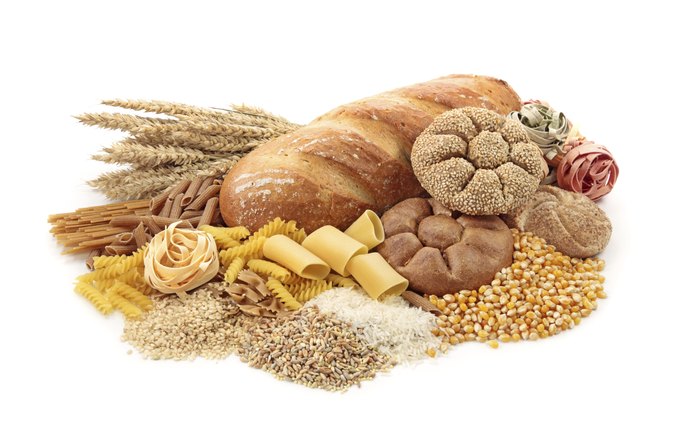
Carbohydrates give us lots of energy. Fibre is good for our digestion. Some examples include: bread, pasta, rice, and other grains.


Fats help our brain and nervous system .Some fats are better for us than others. Good fats include olive oil, salmon, nuts and avocados.
 We have three main meals every day: breakfast, lunch and dinner. We also have two snacks, in the morning and in the afternoon.
We have three main meals every day: breakfast, lunch and dinner. We also have two snacks, in the morning and in the afternoon.

DON'T FORGET...


Water is very important. About 75% of our bodies is water. We should drink 1.5 litres of water every day (that's 6 glasses)!

Healthy vs. Unhealthy Habits:
HEALTHY 👍
Sleeping 8-10 hours.
Go to bed early.
Wash your hands (before you eat and after you go to the toilet)
Exercise (1 hour every day)
Brush your teeth (at least twice a day)
Take a bath or shower.
UNHEALTHY 👎
Sleep less than 8 hours.
Go to bed late.
Don't wash your hands.
Be lazy.
Don't exercise.
Eat fast food.
Smoke.
Circulatory system
The heart and circulatory system (also called the cardiovascular system) make up the network that delivers blood to the body's tissues. With each heartbeat, blood is sent throughout our bodies, carrying oxygen and nutrients to all of our cells.
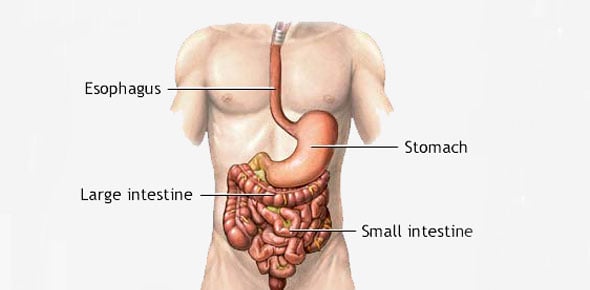
 Human Digestive System
Human Digestive System
Our body needs food to provide it with energy, vitamins, and minerals. However, in order use food, we must first break it down into substances that the various organs and cells in our body can use. This is the job of our digestive system. The digestive system acts in stages to digest our food.
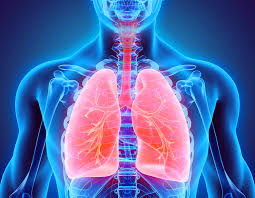
 Respiratory system
Humans breathe through something called the respiratory system. This system is made up primarily of our lungs and windpipe.
Respiratory system
Humans breathe through something called the respiratory system. This system is made up primarily of our lungs and windpipe.
Our body is a very complex system. One of the main things it needs is energy. We get the oxygen to our cells with the respiratory system and by breathing.
Reproductive Organs
*Remember to study the names (and spelling) of the reproductive organs.
MALE: 1 testicles 2 urethra 3 penis
FEMALE: 1 ovary 2 uterus 3 vagina 4 vulva


DON'T FORGET...

Circulatory system
The heart and circulatory system (also called the cardiovascular system) make up the network that delivers blood to the body's tissues. With each heartbeat, blood is sent throughout our bodies, carrying oxygen and nutrients to all of our cells.

Human Digestive System
Our body needs food to provide it with energy, vitamins, and minerals. However, in order use food, we must first break it down into substances that the various organs and cells in our body can use. This is the job of our digestive system. The digestive system acts in stages to digest our food.

Respiratory system
Humans breathe through something called the respiratory system. This system is made up primarily of our lungs and windpipe.
Our body is a very complex system. One of the main things it needs is energy. We get the oxygen to our cells with the respiratory system and by breathing.
Stages of Life
*Remember to study the names (and spelling) of the stages of life.
- Babies need a lot of attention and help from their parents.
- Children are able to learn lots of new things.
- Adolescents continue to grow and their bodies change a lot.
- When we're adults, our bodies stop growing.
- Elderly people have a lot of experiences but they sometimes need help to do things. We can learn a lot from them.
UNIT 1: INTERACTION
PARTS OF THE BODY


THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
The nervous system is made up of the brain, the spinal cord, and a large network of nerves that covers all parts of the body.
Together the nervous system helps different parts of our body communicate and allows our brain to control what is going on.

The biggest part of the brain is the cerebrum. The cerebrum makes up 85% of the brain's weight, and it's easy to see why. The cerebrum is the thinking part of the brain and it controls your voluntary muscles — the ones that move when you want them to. So you can't dance — or kick a soccer ball — without your cerebrum.
Next up is the cerebellum. The cerebellum is at the back of the brain, below the cerebrum. It's a lot smaller than the cerebrum at only 1/8 of its size. But it's a very important part of the brain. It controls balance, movement, and coordination (how your muscles work together).
Another brain part that's small but mighty is the brain stem. The brain stem sits beneath the cerebrum and in front of the cerebellum. It connects the rest of the brain to the spinal cord, which runs down your neck and back. The brain stem is in charge of all the functions your body needs to stay alive, like breathing air, digesting food, and circulating blood.
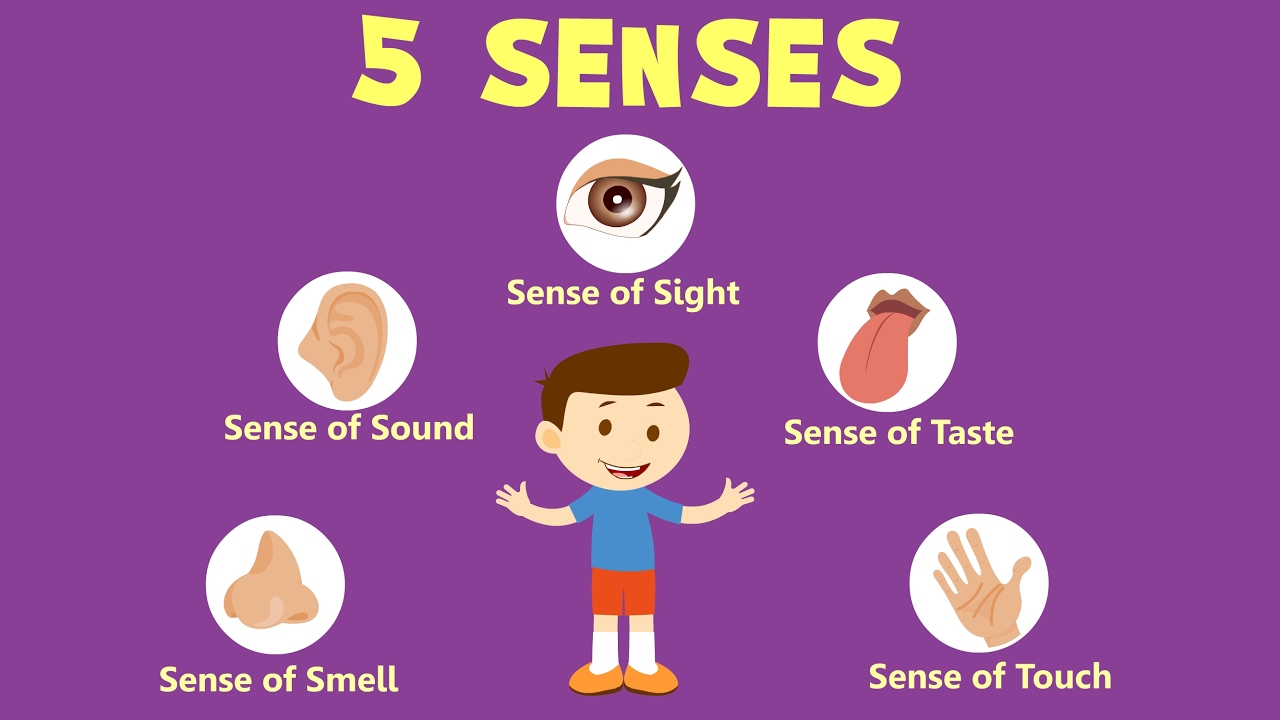
We have 5 SENSE ORGANS...






























Where can I find the homework?
ReplyDeleteSusana Del Barrio.